| Value including complex |
| Full elliptic integral of 1 sort |
| Full elliptic integral 2 sorts |
Elliptic integrals first appeared in the problem of determining the perimeter of an arbitrary ellipse .
In the general case, the integral is called elliptic
where is a rational function of \(x\) and \(y\) , and \(y ^ 2\) - polynomial of the third or fourth degree fromxx
Transformations are known that allow expressing any elliptic integral in terms of the integral of a rational function xx and the following three canonical integrals.
Elliptic integral of the first kind
Elliptic integral of the second kind
Elliptic integral of the third kind
Here
\(\varphi \) - amplitude
\(k \) - module
\(n \) is the parameter of the elliptic integral (of the third kind)
Integrals for which the amplitude \(\varphi = \frac {\phi} {2} \) are called complete. For integrals of the first and second kind, the notation is used, respectively.
An additional module is used, which is equal by definition
In tables of elliptic integrals, it is customary to express the amplitude in degrees. In addition, often quantities F, E, K, Ethe F ,E ,the K ,E are considered as functions of the modular angle - the angle replacing the modulus and expressed in degrees:
In this way
When calculating \(K (k)\) one of the most effective is the iterative method ofarithmetic-geometric mean (AGS). Starting from a couple \( a_0 = 1\) ; \(b_0 = k_1 = cos (\alpha)\) are the following arithmetic mean and geometric mean, which form two converging sequences:
The process ends with this nn for which aa and bb match. Sought value KK is determined by the formula
There is an even simpler formula, with kk tending to unity.
The calculation of the full elliptic integral of the second kind is carried out according to the same scheme as in the case of the integral of the first kind, using differences
\(c_n = \frac {a_n-b_n} {2}, n = 1,2,3 .....\)
obtained at each iteration. Then
Where \(c_0 = k\)
Bot, calculates the values of the full elliptic integral of the first and second kind, for any values kk
With this bot, we can easily determine the perimeter of an ellipse , as well as the length of the arc of any second-order curve .
Some examples
If \(x = i\)
| Complete elliptic integral of the first kind |
%20=%201.3110287771461) |
| Complete elliptic integral of the 2nd kind |
%20=%201.910098894514) |
I would like to note that if you check according to the data provided by the site www.wolframalpha.com it turns out that it has different values. This is due to the fact that on that site, the argument is first squared, that is, there the values are shown for the value \(i ^ 2 = - 1\)
| Complete elliptic integral of the first kind |
%20=%201.6857503548126) |
| Complete elliptic integral of the 2nd kind |
%20=%201.4674622093395) |
and one more
| Complete elliptic integral of the first kind |
%20=%200.19712334640198-0.43443093218712i) |
| Complete elliptic integral of the 2nd kind |
%20=%200.098367068970897+7.7518095000745i) |
If you somewhere found an error in the calculations, please kindly report it. Thank!!!
Good luck!


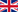
%20dx)
=\int_{0}^{\varphi}%20\frac{%20dx%20}{sqrt{1-k^2sin^2(t)}})
=\int_{0}^{\varphi}%20\sqrt{1-k^2sin^2(t)}dt)
%20=%20\int%20\limits_{0}^{\varphi}\!\frac{d\varphi}{(1+n%20\sin^2%20\varphi)%20\sqrt{1-k^2\sin^2\varphi}})
=F(\frac{\pi}{2},k))
=E(\frac{\pi}{2},k))

)
)
)



=\frac{\pi}{2a_n})
=ln(\frac{4}{k_1}))
=(1-\frac{1}{2}\sum_{n=0}^N2^nc_n^2)K(k))